Renault Vivastella First generation
 |
|
|
Production |
1929–1934 |
|
Class |
Luxury car |
|
Body style |
4-door saloon |
|
length |
4450-5000mm |
|
wheelbase |
3107-3390mm |
|
Engine |
I6 3180 cc, 65HP |
|
Transmission |
3-speed manual |
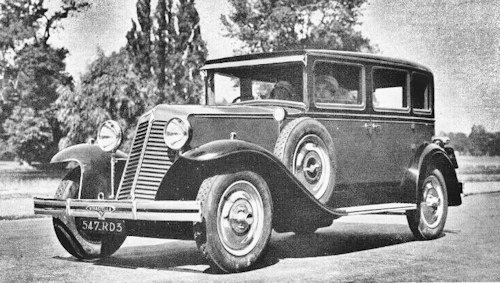
The Renault Vivastella First generation was an luxury car introduced by Renault in October 1928 and produced for the model years 1929 to 1934.
History
The Renault Vivastella was an interwar passenger was introduced at the 22nd Paris Motor Show in October 1928 as a more luxurious version of the Renault Vivasix.
The car was changed with often in the 1930s with the car model manufactured by Renault . The type codes were Type PG , Type ZA .
In 1929 The "Renault Vivastella Type PG2" The water-cooled six- cylinder engine with 75 mm bore and 120 mm stroke had a displacement of 3181 cm³ . The engine power was transmitted to the rear axle via a cardan shaft .The radiator was placed behind the engine. At the front of the vehicle was a rhombus , Renault's trademark, and a star , like all Stella variants. The front bumper consisted of two tubes. The difference to the basic model consisted u. a. in dual wipers , door pockets and chrome hubcaps . with claimed output of 52 HP.
Type PG 3 .This model appeared in 1929 as a 1930 model. The cooler was now placed in front of the engine. The radiator grille was arranged slightly obliquely. There were no vents on the sides of the hood yet. The track width was 144 cm at the front and 145.4 cm at the rear. The wheelbase of the five-seat bodies was 310.7 cm and that of the seven-seat bodies 334.7 cm. As before, the sedan and Pullman sedan have survived.
By 1930 The "Renault Vivastella Type PG4 was 15 cm larger than the previous model. In 1932, a 65 horsepower engine was introduced.On the sides of the hood were vertical air vents. The front bumper consisted of two tubes. In addition to the sedan and Pullman sedan, a convertible was available. The vehicles with the short chassis were 450 cm long and 170 cm wide.
This version was presented at the Paris Motor Show in October 1932. The engine produced 65 hp . Presumably three ventilation flaps of the same size in the sides of the bonnet and a one-piece straight front bumper were distinguishing features. At the beginning of 1933, the SA version with a different engine mount was added to the range. 1933, the new series Type PG5 (5 seater) and PG7 (7 seater) The "Renault Vivastella Type ZA2" was introduced; This version received its approval on December 15, 1933. The cylinder bore, enlarged to 80 mm, provided 3619 cm³ displacement and 85 hp. Wheelbase and track width remained unchanged. The turning circle was given as 14 meters. The chassis weighed 1150 kg. There were four ventilation flaps of different heights on the sides of the hood.it had a radiator behind the engine, which was enlarged in Spring 1934 to 3620cc, now giving a maximum output of 80HP. The 6-cylinder units shared the same 120mm cylinder stroke length, but the bore (cylinder diameter) on the larger engine was increased by 5mm to 80mm. ZA3 version appeared in October 1934. There were four horizontal air vents in the sides of the hood. Between the two short front bumpers there was space for the license plate number . Only sedan and Pullman sedan were on offer. With a wheelbase of 313 cm or 339 cm, the vehicles were 478 cm or 500 cm long and 180 cm wide. Production ended on March 26, 1935.
Although a new more modern Vivastella was introduced for 1934, the earlier model continued to be listed, at an attractively lower price, in the catalogue. It incorporated most of the new mechanical elements of the new car, but used the older much more vertical looking bodywork.Derivative models, the Renault Vivasport and the sporting Renault Viva Grand Sport were also introduced.
