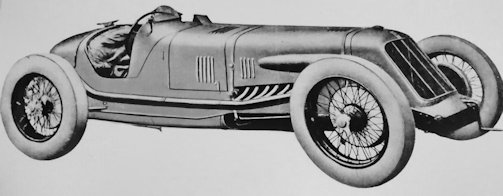
Maserati 8C Race car
 |
|
|
Builder |
Maserati |
|
Production |
from 1928 to 1933 |
|
Class |
Race Car |
|
Engines |
1.1 to 2.8 litres |
|
Length |
3855 mm |
|
Height |
1200 mm |
|
weight |
820 kg g |
The 8C is a racing car built by Maserati from 1931 to 1933. It was also known as the “8C 2800” and “8C 3000”, based on the installed engine displacement. It was designed to be the definitive version that participated in the Grand Prix.
History
Alfieri Maserati Officine Maserati founded constructed after the end of World War first racing car for Isotta Fraschini and Diatto. When Diatto gave up his motorsport commitment in the early autumn of 1925 because of economic difficulties, Alfieri Maserati took over the Diatto race cars he developed for free in September 1925 and continued the motorsport program from 1926 under his own name. The first Maserati, the Tipo 26, was a further development of this Diatto model. Maserati drove the Tipo 26 himself in some races; several copies were also sold to private customers. The Tipo 26 was powered by a series eight-cylinder with 1.5 litres and 2.0 litres (26B) displacement, the power was between 115 and 130 hp.
The 8C was designed by Alfieri Maserati in the early 1930s, but Alfieri died before the project was completed. The car was rear-wheel drive with a front engine. Engine development continued even after Alfieri's death, and the car was ready for competition in 1932.
The Maserati 8C was after the Tipo 26 and the V4, the third race car model, developed and built by the Italian car manufacturer Officine Maserati. Maserati offered the model in four different variants with engines between 1.1 and 2.8 litres. The model family reached a total circulation of "a dozen copies." The 2.5- and 2.8-liter versions are considered the most powerful single-engine racing car of its time. With them, Maserati established itself temporarily as the most successful Italian racing car manufacturer. The Maserati 8C was an evolution of the Tipo 26. The chassis largely corresponded to the previous model; it had been "only marginally revised". As the Tipo 26 8C had a lead frame, which was formed from tubes with U-profiles. This was lowered in the middle section and had three suspension points for the engine. There were rigid axles in front and behind. The rear axle was suspended from semi- elliptic steel leaf springs.
By 1930, three cars were being made; the 8C 2500 with 175 b.h.p. at 6000 r.p.m., which took part in road trim in the Irish Grand Prix and Ulster Tourist Trophy races of 1931, coming second in the former with a four-passenger body; the 8C 1500, which was an improved (shorter, more substantial) Tipo 26, with 120 b.h.p.; and the 8C 1100, which won its class, suitably road-equipped, in the 1931 and 1932 Mille Miglia. With Its 100 b.h.p. at 5500 r.p.m., which with a weight of under 16 cwt. gave a maximum speed of 115 m.p.h. All three cars were offered in sports trim if required. All used the basic two overhead-camshaft, straight- eight engine with Roots-type super-charger, aluminium pistons, tubular
connecting rods, and two valves per cylinder.
As an evolution of the Tipo 26 from 1929, the 8C, which was able to establish itself in contrast to the simultaneously constructed, complicated 16-cylinder V4 model quickly and achieved some racing successes. The 8C was the last Maserati, whose conception of the company's founder Alfieri Maserati came. After Alfieri's death, his brother Ernesto developed the 8C into the more powerful 8CM with a 3.0-liter engine. As drive different size large eight-cylinder engines were provided, all based on the construction of the Tipo-26 engine. The gearbox housing and the brake system of all versions was manufactured by Maserati at Isotta Fraschini.
Maserati 8C-1500
The first model of the 8C series was the Maserati 8C-1500. It was built in 1928. Maserati joined the slightly revised chassis of the 8C with the well-known 1.5-liter eight-cylinder engine of the Tipo 26. He made about four copies.
Maserati 8C-1100
1929 appeared with the 8C-1100 a weaker motorized variant. The engine had a displacement of only 1,077 cc. It was basically the engine block that had already been used in the Tipo 26 and the 8C-1500. Displacement was reduced by a stroke reduced to 51 mm. The engine power was about 100 hp (74 kW). The small Maserati model was mainly to compete with the compact contemporary French racing cars Salmson, but could not prevail against them, as he was much heavier. The 8C-1100 appeared only at individual races.
Maserati 8C-2500
The most widely used model was the 1930 introduced Maserati 8C-2500, which is alternatively referred to as Tipo 26M. This had a 2495 cc version of the eight-cylinder engine with two overhead camshafts. The combustion chambers were hemispherical in shape. Different versions were built with compaction ratios between 7: 1 and 8: 1. The mixture prepared a simple Weber carburettor. As with previous models, the engine was charged with a Roots compressor. Depending on the source, the engine output was 175 to 195 HP (129 to 143 kW). The body was very similar to the V4. She also had a sloping grille. Most sources assume that Maserati made a total of eight copies of the 8C-2500; There were also some older Tipo 26 models, which were later equipped with the new eight-cylinder engine.
A copy of the 8C-2500 was delivered as a sedan. The construction came from Castagna. Additional road versions of the 8C-2500 were planned, including a Castagna Cabriolet and several open and closed versions of Zagato; none of them were actually realized.
Maserati 8C-2800
The 8C-2800 was the last evolution of the 8C family. He appeared in the fall of 1931. This had a 2795 cc engine, the power of the factory with 198 hp (146 kW) was specified. Observers consider this value to be exaggerated, assuming outputs between 175 and 190 hp (129 and 140 kW). The maximum speed was determined at 233 km / h.
It was the end result of the evolution of the Tipo 26, built to compete with the Alfa Romeo 8C Monza, the Alfa Romeo Tipo A and the Bugatti Tipo 51. The model had installed the Tipo 26 M engine, with the bore increased by 4 mm to reach a displacement of 2.8 L and therefore deliver a power of 205 HP at 5500 rpm. The engine was designed in collaboration with the Weber carburettor manufacturing company. The bodywork it was compact and had a low profile, which led to good aerodynamics. The maximum speed was between 210 and 230 km/h. Four Tipo 26 M of the 14 examples produced were equipped with a 2.8 L engine and equipped with a renewed bodywork, thus becoming the "8C 2800”. The ignition was single with Scintilla magneto. The fuelling was forced with a Roots type compressor and a Weber ASS brand carburettor, mounted upstream of the compressor itself. The distribution was two valves per cylinder arranged in a 90° V, with a double overhead camshaft. The engine was an in-line eight-cylinder with a displacement of 2811.9 cm³. The bore and stroke were 69 and 94 mm respectively, and the compression ratio was 5.5:1. Lubrication was forced with delivery and recovery pumps. The cooling system was water-circulating with a centrifugal pump.
The bodywork was a two-seater in aluminium. The frame was made up of two longitudinal members with steel profile crosspieces. The brakes were drum brakes on the wheels with mechanical control, while the suspensions were with leaf springs and friction shock absorbers. The steering was with worm screw and toothed sector. The transmission consisted of a four-speed gearbox plus reverse.
The first race was on 21 June 1931 at the French Grand Prix.
The 8C 3000
In 1933 the model won the French Grand Prix with Giuseppe Campari, and Henry Birkin took third position in the Tripoli Grand Prix. This did not win any other races. Other pilots were Luigi Fagioli and Baconin Borzacchini.
The engine had a displacement of 2991.4 cm³ which delivered 220 horsepower at 5500 rpm. It was an in-line eight-cylinder and was inspired by the in-line four-cylinder fitted to the Maserati 4CTR. The bore was 69 mm, while the stroke was 100 mm. The compression ratio was 5.26:1. The car reached a maximum speed between 220 and 240 km/h. The ignition was by magneto Bosch or Scintilla, while the fuelling was forced with a Roots type compressor with a Weber 55AS1 carburettor upstream of the compressor itself. The distribution was two valves per cylinder at 90° with two overhead camshafts.
The chassis was the same as that mounted on the Tipo 26M., with two longitudinal members with crosspieces made of steel profiles. The gearbox was manual with four speeds and had several points in common with the one mounted on the Fiat 522. It was the cause of complaints from pilots due to the intense vibrations of the lever. The tires used were initially Dunlop’s, then replaced by Pirellis. The bodywork was a two-seater in aluminium. The suspension was leaf spring with shock absorbers friction. The steering was with worm screw and toothed sector.

Racing inserts
Although the small 8C-1100 was able to win individual class victories - including the Mille Miglia 1931 - but achieved no overall victory. Only the heavily motorized versions 8C-2500 and 8C-2800 were regularly successful in races.
In 1930, the 8C-2500 was the preferred model of the Maserati factory team. Occasionally, even older Tipo 26 units and the V4 were used, but they achieved no success. The 8C-2500 appeared for the first time at the Targa Florio on May 6, 1930. Here were four copies with Luigi Arcangeli, Baconin Borzacchini, Luigi Fagioli and Ernesto Maserati at the start. Arcangeli and Fagioli dropped out prematurely, Maserati came in eighth and Borzacchini in eleventh place finish. The first victory scored an 8C at the 1930 edition of the Gran Premio di Roma at the Circuito Tre Fontane that Arcangeli won. This was followed by double victories at the Coppa Acerbo (Arcangeli and Ernesto Maserati), the Grand Prix of Monza (Varzi and Arcangeli) and in October 1930 at the Spanish Grand Prix (Varzi and Aymo Maggi ).
In 1931, Maserati was unable to match the previous year's performance with the 8C-2500. In the first half of the year, the Bugatti vehicles dominated the Grand Prix. Apart from winning the Monza Grand Prix (Fagioli), the Maserati factory team only achieved a couple of second places with the 8C-2500, including Tunisia and Monaco (both Fagioli) and the Marne (René Dreyfus). Otherwise, there were a number of technical failures. In the following years, many private drivers used different versions of the 8C-2500.
The more powerful 8C-2800 debuted at the Monza Grand Prix in September 1931.
Technical
-
Maserati 8C Technical details and specifications (1928-1933)
ENGINES:
Maserati 8C-1100.
Water cooled,
eight vertical cylinders in line
51 x 66 mm.
1078 cc.
Roots supercharger.
Overhead valves operated by two overhead camshafts.
Four forward speeds.Maserati 8C-1500
1.5-liter
eight-cylinder engineMaserati 8C-2500
2495 cc
eight-cylinder engine
two overhead camshafts
hemispherical combustion chambers
compression ratio: 7: 1 and 8: 1.
Weber carburettor.
Roots compressor.
8C-2800
2795 cc engine
in-line eight-cylinder
bore and stroke were 69 and 94 mm
compression ratio was 5.5:1.
Weber ASS carburettor
ignition Scintilla magneto.
two valves per cylinder 90° V
double overhead camshaft.© Motor car History
