USA
- Details
- Parent Category: Motor car History
- Category: USA
Brogan (B & B Specialty Company)
Automotive manufacturer Rossmoyne , Ohio .USA from 1946 to 1951

Brogan was an American automobile brand that was built from 1946 to 1951 by the B & B Specialty Company in Rossmoyne , Ohio .
The first Brogans was built in after the second world war from 1946 to 1948. It was a tiny, two- seated three-wheeled roadster (a single wheel in front) that resembled a bumper car. It was powered by a front-mounted Onan air-cooled two-cylinder engine developing 10 bhp (7.4 kW) of power. The wheelbase was 1524 mm. The selling price was US $ 600.
In 1948, the Brogan Package Car was added, with which loads could be transported.In 1949, the first Brogan was replaced by the Broganette . The offered four passengers space and had a single rear wheel. The engine was the same.
- Details
- Parent Category: Motor car History
- Category: USA
Atterbury Motor Truck Company
Automotive manufacturer Buffalo , New York , United States from 1904 to 1935

Atterbury Motor Truck Company , previously Auto Car Equipment Company and Manufacturing Company and Atterbury Motor Car Company , was an American manufacturer of motor vehicles .
History
John B. Corcoran, George W. Atterbury and Elmer B. Olmstead founded in 1904 the car car equipment company for the production of commercial vehicles . The seat was in Buffalo in the US state of New York . 1907 saw the first cars , which were marketed as an Auto Car . Later, the name changed to Auto Car Manufacturing Company and in December 1909 to Atterbury Motor Car Company . The reason given was the likelihood of confusion with the Autocar Company. 1911 emerged again some cars, now as Atterburywere offered. In March 1912, the next name change followed in Atterbury Motor Truck Company . It was not until 1935 that truck production ended.
The trucks until 1908 had either gasoline or electric motors . The maximum value is 6 tonnes, although it remains unclear whether this was the payload or the gross vehicle weight. In addition, buses are specified. From 1910, the trucks had payloads between 1.5 tonnes and 7 tonnes. Various gasoline engines from Buda , Continental and Lycoming powered the vehicles.
The car model of 1907 was a large sedan that could accommodate seven to ten people. A six-cylinder engine with 60 hp powered the vehicles.By 1911 followed by a ten -seater touring car .

- Details
- Parent Category: Motor car History
- Category: USA
American & British Manufacturing Corporation (Porter)
Automotive manufacturer Fairfield County , Connecticut , United States
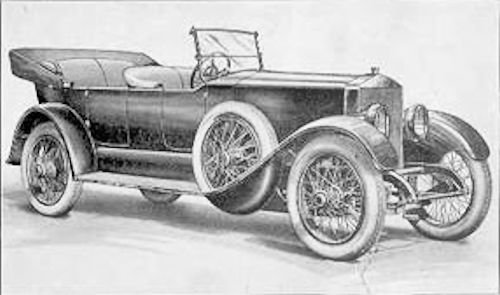
The American & British Manufacturing Corporation (A & BMC) was an American defense and industrial company that manufactured guns for the US Navy , steam engines and motor vehicles. Trucks and Avant-Trains were as American & British or A & B.
From 1919 to 1922, the luxury cars Porter Model 45 and Porter Model 46 were manufactured, which were among the strongest and most expensive in the US market.The Porter Knight was not a model of the American & British Manufacturing Corporation .
History
The company was founded on May 23, 1902 as the "American Machine & Ordnance Co." in New York and renamed the "American & British Manufacturing Co." on November 28. The activities of the company was the production of firearms , ammunition , steam engines , Glühkopfmotoren , automobile engines , marine engines and repairs of all kinds indicated. To the company owned the operations of listed Corliss Steam Engine Works in Providence ( Rhode Iceland ) and American Ordnance Works in Bridgeport . A main owner of the company was theInternational Power Co. The Corliss Steam Engine Company was a well known manufacturer of Balancing - steam engines after by George Henry Corliss
Under the brand names American & British and especially A & B created between 1914 and 1922 two commercial vehicle series, one of them as Avant-Train with gasoline electric drive . These components were used to subsequently motorize existing horse-drawn vehicles. Such conversion was useful only for very expensive cars. For Avant-Trains , there was quite a demand, such as in firefighting organizations. Motorized firefighting vehicles were very expensive to buy and retrofitting was a cost effective alternative. The conversion of existing, newer horse drawn steam boosters increased their efficiency and uptime while the organization could cut costs by eliminating horse keeping infrastructure. The market for these vehicles was by nature not large and specialized. Therefore, there was less competitive pressure in this niche. However, it was not sustainable and could only exist for a short time.
During the First World War , A & BMC supplied ammunition to the American armed forces. With the end of the war, A & BMC lost its armaments orders and the company had to seek compensation for the resulting loss of production. This may be the reason that they were interested in car production. To the machines and commercial vehicles came a car production. It is not known how the contact with FR Porter came about and what the conditions for the production looked like. Porter was pleased with his design work at Curtiss and did not want to worry about a whole production. Production and sales of Porterreferred to A & BMC . It was based on the construction of the FRP . Although she was now several years old but still modern. The Porter with its high-performance engine of, depending on the source, 100 to 125 bhp still the strongest engine on the market. The only sports cars that came close to performance were the equipped with modified Duesenberg engines Argonne, Biddle, Meteor, ReVere and Roamer, which made up to 103 bhp (up to 106 bhp in ReVere). A & BMC adapted the vehicle concept only in details and did not use short versions. The porter was a very big car with an imposing 142 inch wheelbase. That only 36 copies were produced between 1919 and 1922 must have been a bitter disappointment. This was due to the complex production with many still hard-to-find materials, a horrendously high list price and a short but severe recession, which is due to the farm crisis.
In 1925, the American & British Manufacturing Corporation and Franklin Machine Company (unrelated to HH Franklin Manufacturing Company ) were merged. Thus, the William A. Harris Steam Engine Company owned by Franklin Machine in the new group. Both Harris Steam Engine as Franklin Machine had built steam engine with Corliss rotary vane technology after the expiry of patent protection.
Motor Vehicles
Under the brand names American & British and especially A & B emerged between 1914 and 1922 and commercial vehicles . One source called for the start of vehicle production already in 1906. About these vehicles are hardly any information before. Two trucks are mentioned with a payload of 3 sh. tn. (2720 kg) respectively 5 sh. tn. (4530 kg), which was then classified in the middle or heavy class. Technical data is not available. The competition in the commercial vehicle sector was then very large with dozens of providers.
Others pushed new to the market to make up for the sudden loss of armaments orders. Most of these manufacturers - and probably A & BMC - were " assembler " that their vehicles from components and standardized products together established that they found in a free market.
A second series of the A & BMC consisted of an Avant-Train . This known as a motor wheel or Fore car device is used to give a wagon or a coach later self-propelled. The Avant-Train typically consists of a short chassis with a driven and steerable front axle and the cab and replaces the turntable with wheels and drawbar of the wagon. The resulting from the assembly motor vehicle is often called Avant-Traindesignated. Such vehicles had their greatest spread in the period of the oncoming motor vehicle in the years between 1905 and 1920. Because of the complex drive technology, they were quite expensive; the conversion was therefore worthwhile only on valuable objects. A typical application for Avant-Trains was found in firefighting. Often expensive and durable steam spraying were available. Their conversion increased the efficiency of the syringes and extended their life; A savings effect resulted from the reduction of horse keeping. By its very nature, the market was not large and foreseeable even unsustainable. Discontinued, horse-drawn syringes were increasingly replaced by appropriately equipped trucks.
A special feature of the A & B Avant-Train was its gasoline-electric drive . Here, a conventional internal combustion engine produces power that is passed on to a power generator. This in turn feeds each an electric motor in each front wheel. The mechanism requires neither transmission nor clutch. A similar concept was used by the Bourne Magnetic Truck Company in Philadelphia for their otherwise conventional rear-wheel drive trucks. The most famous car with this so-called Entz-drive is the Owen Magnetic .
Porter automobiles Finley Robertson Porter and the FRP
Finley Robertson Porter (1871-1964) of Lowell, Ohio had made a name for himself as the designer of the Mercer Type 35 , from which he derived the successful sports car Raceabout . He then made off with the Finley Robertson Porter Company independently, with the 45 FRP model the strongest US automobile produced this time. The First World War led to a takeover of the operation by the government and the setting of the complex built model 45 for a very small quantity. During the First World War belonged FR Porter as a test engineer to the team in Dayton ( Ohio ) the Liberty engine developed.
After the war, Porter was no longer interested in car manufacturing and took over the position of chief engineer of the Curtiss Engineering Company in Garden City (New York) . The Finley Robertson Porter Company was settled in 1918.
Porter Model 45 and 46
A contract for the exploitation of its automotive patents, Porter awarded to American & British Manufacturing . She organized the production; The sales organization was the New York-based automobile trading firm Morton W. Smith Company . Robert B. Porter , his son and from 1915 himself a designer for FRP , took over the technical management as chief engineer.
Technically, this vehicle was very similar to the FRP and components and components of the Finley Robertson Porter Company appear to have been used up. The performance was specified at 125 bhp (93.2 kW). Instead of the three chassis lengths with 110, 130 and 140 inches (2794, 3302 or 3556 mm) wheelbase there was now only one with 142 inches (3607 mm). That was two inches more than the largest FRP had. The vehicle, whose concept dates back to 1914, became obsolete and the Porter became an anachronismwhich included adhering to the right-hand drive . Porter was the last US car brand to hold onto it; even Pierce-Arrow , who was focused on a particularly conservative clientele, was now a left-hander .
Despite the powerful engine - probably still the strongest car engine in the US - the mighty chassis was not well-suited for athletic customers, but it was a very good base for display cars. Known are superstructures of leading coachbuilders such as Brewster , Demarest or Fleetwood . As with the FRP presented Holbrook working bodies, including even a Speedster. With 12 vehicles, however, the karossierte Blue Ribbon Body Company most in Bridgeport Porter . The design has been modernized and received a stricter line. The radiator's outline was reminiscent of Rolls-Royce.
The Porter was made from 1919 to 1922; depending on the source, only 34, 36 or 40 copies were produced. Cost already bare chassis US $ 6750 . The car could not withstand the enormous competitive pressure in this market segment and the economic crisis of 1922.
For the first copies of the Porter , components taken over from the FRP were used up. It may explain the model number Model 45 . Accordingly, Model 46 would have been built from new components. In any case, technical differences are not known or too minor to be explained in the available sources. Therefore, unless otherwise noted, the specifications refer to the FRP Model 45 .
The engine was a marvel of lightweight construction and weighed only 580 lb (about 260 kg). It consisted predominantly of aluminum alloys; Crankshaft , camshaft and even the valve tappets were also hollow. The engine has one overhead camshaft and one intake and exhaust valve per cylinder ; Isolated information regarding four-valve technology unlikely to occur and are only mentioned in isolated sources. When closed, the valves formed a hemispherical end of the combustion chamber. The crankshaft was mounted in triplicate
The bore was 4.6 inches (about 117 mm), the hub 6¾ inches (171 mm). This gave a capacity of 448.7 ci (7353 cc); occasionally called displacement of 454 ci may be due to rounded output ground.
For the chassis, Porter used new steel alloys. For customers who wanted an individual body, the bare chassis was also available, which was clad at the coachbuilder of his choice.
The long chassis was a very good base for representation cars. Familiar structures of leading coachbuilders such as Brewster , Demarest or Fleetwood . As with the FRP, Holbrook provided bodyshops, including a Speedster. With 12 vehicles, however, the karossierte Blue Ribbon Body Company most in Bridgeport Porter . The design has been modernized and given a stricter lines. The outline of the radiator now reminded Rolls-Royce.
There are no exact numbers about the number of pieces. It is clear that material has been purchased for 10 FRP vehicles. Depending on the source, between 3 and 12 FRP have been produced ; the Seal Cove Museum names nine. The Porter was built from 1919 to 1922. Depending on the source, only 34, 36 or 40 copies were produced.
The low volumes of the FRP are understandable due to the production of virtually all components in the house and because of the aborted production after the takeover by the government. The fact that only so few Porters were built, is due to a misjudgment of the market, the difficult economic environment and the fact that the concept of the Porter was no longer new and high-priced four-cylinder automobiles were less and less in demand. This experience was also made by those manufacturers who used similarly exotic Duesenberg Walking Beam and Rochester-Duesenberg four-cylinders, including Argonne , Biddle , Kenworthy, Meteor , Revere , Richelieu and Roamer .

- Details
- Parent Category: Motor car History
- Category: USA
Devin Enterprises
Automotive manufacturer El Monte,California USA from 1955 to 1964

Devin Enterprises was an American automaker, which was 1955 to 1964 based in El Monte (California) . Founder was Bill Devin. Devin was mainly known for its elegant fiberglass bodywork, but also offered complete automobiles.
Bill Devin was born in 1915 in Rocky, Oklahoma, USA. Bill Devin started building cars early in his life. He was also a very well known and successful racer.
In 1954, Bill Devin decided that he could build cars at least as well as anyone, especially the Europeans. He converted a chicken coop into a workshop and began constructing the legendary Devin Panhards. He worked with polyester bodies, which in the early 1950s was still very innovative and a development of NASA. Devin learned the art of making polyester bodies very fast. He used this novel material specifically to reduce the weight of his racing sports car.
Another milestone was the further developed Panhard engine, which was equipped with a belt-driven overhead camshaft. Devin forgot to patent this idea, since paperwork was an abomination to him.
The next chapter in Bill Devin's life is probably the best known. The attractive and in several variations individually available Devin bodies were based on the design of the Ferrari 750 Monza, respectively the Erminis. With these bodies, a variety of chassis could be equipped, from the small Crosley, on the Triumph TR2 / 3 to powered by a Cadillac engine Allard. Devin quickly became the largest and most successful producer of these bodies. With his dealer network he delivered these bodies to Europe, North, Central and South America and even to South Africa.
Devin's competitors in the US back then were companies like Byers, Almquist, Alken, La Dawri, Microbond, Fiberfab, Fibersport, Atlas, Kellison, Alied, Conquest, Victress and Microplas, most of which have long been forgotten. The name Devin, however, held and he stood for top quality at reasonable cost. Devin bodies were always very smooth and the finishing was better than competing products.
Bill Devin built on the basis of the success of the bodies also complete cars with its own lattice frame. The Devin C based on the Chevrolet Corvair and the Devin D based on the Porsche 356 or VW Beetle. With the Devin SS Devin realized his dream to build fast, powerful complete vehicles. The Devin SS became a famous and successful circuit on many racetracks, but the financial success remained.
Models
Devin SS
1955 was presented as the first model of the SS (Super Sport). Its chassis with 2337 mm wheelbase came from Ireland . Then a two-seater roadster body was mounted. The top -mounted V8 engine of the Chevrolet Corvette with 4638 cc developed 220 bhp (162 kW) power and provided for an acceleration of 0-100 km / h in 4.8 seconds and a top speed of 225 km / h. The engine power was transmitted via manual four-speed gearbox from Borg-Warner to the rear wheels. Due to the high selling price of US $ 5950, - only 15 copies could be sold until 1958.
Devin Panhard
Devin modified a Panhard Dyna Z with its 851cc two-cylinder boxer engine by installing modified cylinder heads from the Norton Manx . The two overhead camshaftswere driven by toothed belts . The race car in 1956 won the championship of the Sports Car Club of America (SCCA) .
Devin D
1959 Devin tried with the much smaller model D . The wheelbase of the Volkswagen chassis was 2,083 mm, and the rear was fitted with air-cooled four-cylinder boxer engines from Volkswagen or Porsche . The VW engine had 1191 cc capacity and made 36 bhp (26.5 kW) at 3700 min , the Porsche engine was waiting with 1586 cc displacement and gave 70 bhp (51 kW) at 4500 min from. The sales price of the version with VW engine was US $ 2950. The production figures up to the model setting should amount to 46.
Devin C
In 1961, Devin fitted the chassis and body of the Model D with the six-cylinder boxer engine from the Chevrolet Corvair . This engine was air-cooled and drew from 2376 cc displacement of an output of 80 bhp (59 kW) at 4400 min . The result was called Model C . It was built until 1964; The production figures are not known in this case either.
Further models
- Devin F (based on the Triumph TR3 )
- Devin GT
- Devin-MG
- Roosevelt Devin
- Bandini with Devin body
- Details
- Parent Category: Motor car History
- Category: USA
Chaparral race cars
Automotive race car manufacturer of USA From 1963 to 1970.

Chaparral was a racing car project of Texas racing driver and designer Jim Hall , which existed from 1963 to 1970 .
History
The technically revolutionary vehicles were characterized among others by the first successful use of automatic transmissions (2D, 1966), and huge rear wings (2E, 1966 and 2F, 1967) and the first "vacuum cleaner racing car" (2J, 1970). In this regard, they were pioneers of many other constructions. The Formula 1 took over the rear wing a year later; Brabham copied the "vacuum cleaner" with the Brabham BT46B .
The Chaparral prototypes won some races or fastest lap times in the United States. Powered by Chevrolet V8 engines . A technical highlight was the type 2J of 1970, which also had a two-stroke engine and side skirts. This ILO - snowmobile engine driving two 17-inch fanwith a constant speed of 5000 / min, which sucked the air under the car and provided for an increased contact pressure . The additional contact pressure is given as 900 pounds (4 kN ).
The cars were less known to the European public by the victory of Phil Hill / Joakim Bonnier in 1966 at the Nürburgring than by the numerous miniature models of these racing cars, which were found in every toy store in the late 1960s and early 1970s.
The Chaparral models were named for years with 2 (1963), 2C (1965), 2D (1966), 2E (1966), 2F (1967), 2G (1968), 2H (1969) and 2J (1970).